The QDD Actuator Renaissance
How a 2016 MIT breakthrough spawned the era of $3k humanoids – and why China now dominates the torque supply chain
TL;DR
Platform shift: MIT's 2016 proprioceptive actuator crushed the torque‑to‑weight barrier, just as "Attention" crushed sequence‑modeling cost. QDD quickly became the de‑facto joint for legged robots.
Cost collapse: Average actuator ASP dropped from ≈$3,000 (2015) to <$300 (2025) on 10,000‑unit runs—a >10× deflation driven almost entirely by Shenzhen's motor‑and‑gearbox ecosystem.
Supply‑chain choke: >90% of NdFeB magnets, >70% of compact BLDC stators, and most PCB assembly for QDDs sit inside China. Rare‑earth export controls are the single largest geopolitical risk.
TAM explosion: Legged‑robot shipments will grow 15× ('23–'31E), from 18k units to ≈270k; humanoids will make up two‑thirds of 2031 volume. At 34 actuators per robot, the joint market reaches 9M units / $1.6B by 2031.
Profit pools migrate: Hardware margin compresses toward power electronics and magnets; differentiation shifts to autonomy, fleet orchestration, and domain‑specific data moats.
1. The Spark: MIT's Cheetah Proprioceptive Actuator
In 2016 the MIT Biomimetic Robotics Lab unveiled a 5.8:1 planetary‑gear, large‑diameter BLDC module delivering 58 Nm peak at just 1.8 kg. Torque was read directly from phase current (~1 kHz loop), eliminating load cells or SEAs. The lab open‑sourced the mechanical and control stack in 2017. Within 24 months, Chinese startups cloned the design and began aggressive cost‑down iterations.
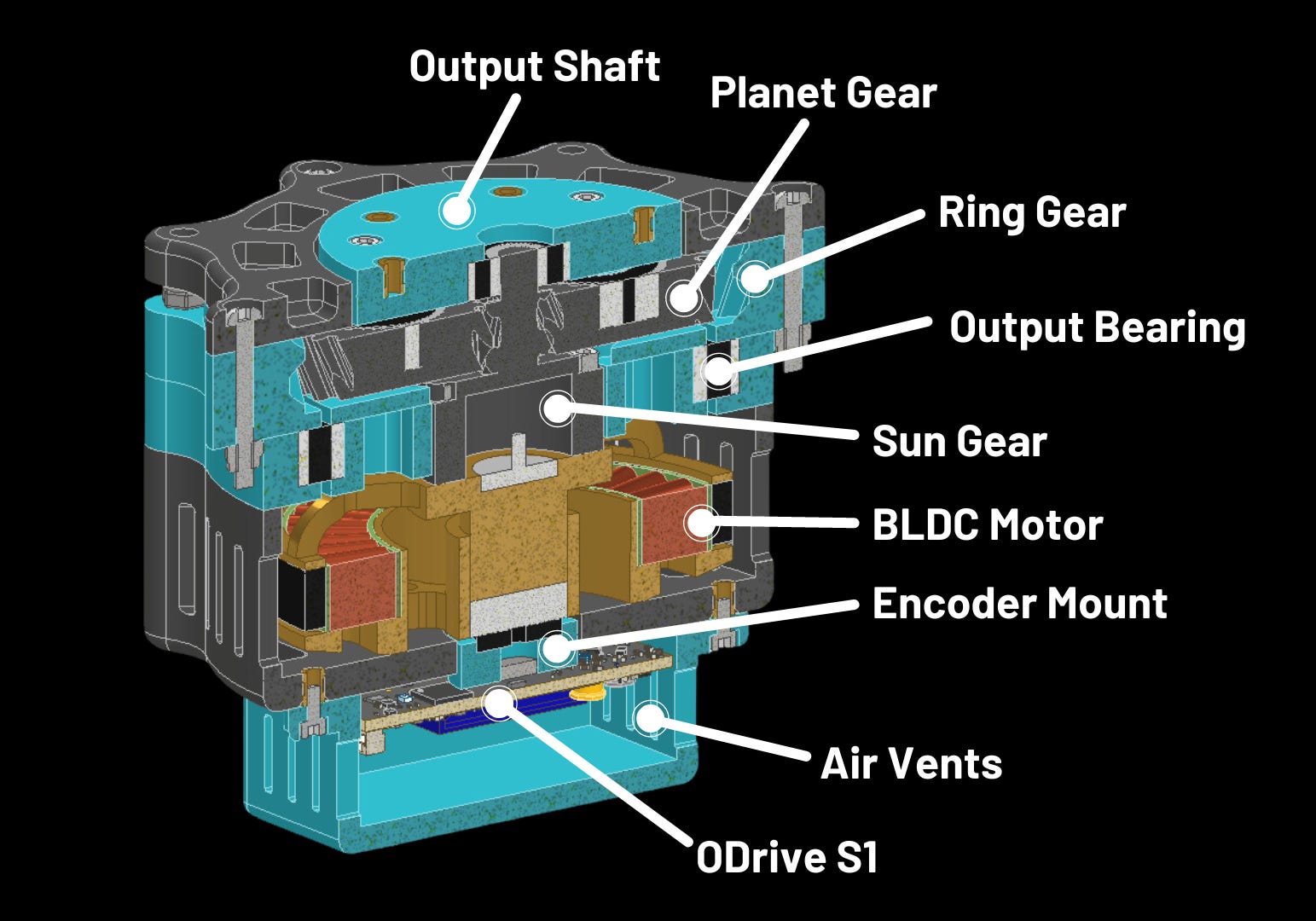 Figure 1 – Cross‑section of a modern QDD actuator
Figure 1 – Cross‑section of a modern QDD actuator
2. Anatomy of a QDD Joint
- NdFeB rotor magnets: torque density ― 24% of cost, 98% made in China
- Stator & windings: electromagnetic core ― 19% cost, 94% China
- Planetary gears: torque multiplier ― 11% cost, 91% China
- SiC/Si MOSFET bridge: power stage ― 14% cost, 58% China
- MCU, encoder, sensors: closed-loop control ― 9% cost, 67% China
- Bearings, housing, misc.: structural support ― 23% cost, 83% China
Key metric: State‑of‑the‑art QDDs deliver 20–40 Nm kg⁻¹ continuous torque and ≥6 kW kg⁻¹ power density—5–8× better than traditional industrial servos.
3. Cost‑Curve Deflation
Nm Trend:
- 2015 – MIT Cheetah v2: $52/Nm
- 2019 – MIT Mini Cheetah: $18/Nm
- 2023 – OpenQDD (DIY): $5/Nm
- 2025 – Unitree Go2 (retail): $4/Nm
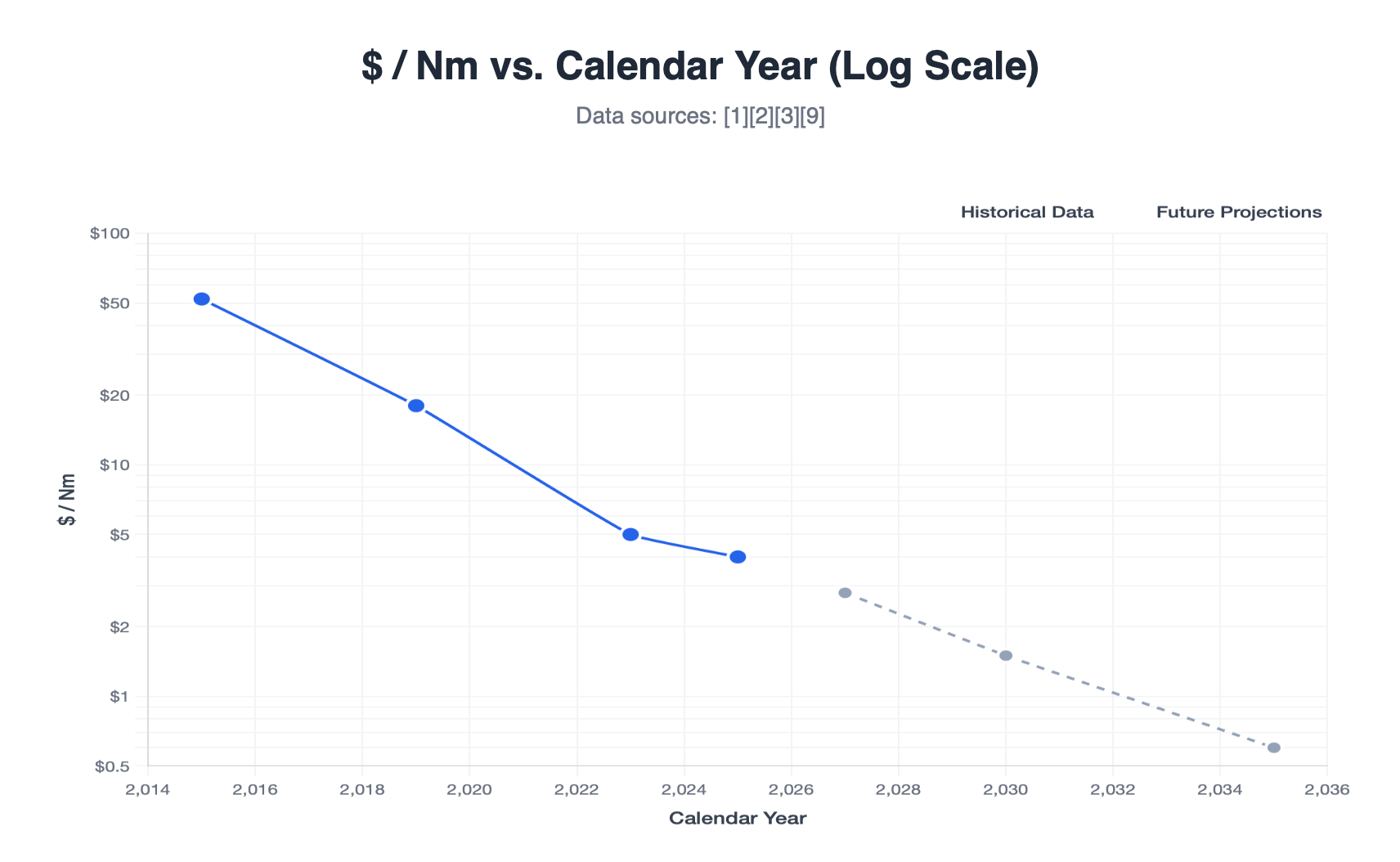 Figure 2 – $ / Nm vs. calendar year (log scale)
Figure 2 – $ / Nm vs. calendar year (log scale)
Three levers drove the slide:
- Magnet oversupply post‑EV boom
- Rapid tolerance gains in Chinese planetary gears
- ODrive‑class open‑source FOC controllers on $12 MCUs
4. Supply‑Chain Choke Points
4.1 Rare‑Earth Magnets
China's October 2024 export licences on NdFeB alloy powder stretched magnet lead‑times from 8 to 21 weeks, adding ~$27 per joint. A full embargo would lift actuator COGS ≈35% overnight and hand pricing power to domestic Chinese vendors.
4.2 Power Semiconductors
SiC FETs (>65 V, <4 mΩ) remain dominated by Infineon, ON Semi, and Rohm. A single humanoid peaks at ~1.3 kW; at $0.20/W SiC die cost, drive silicon is 8% of BOM yet 22% of gross margin. Rohm's Japan fabs are today's bottleneck.
4.3 Gear & Bearing Quality
IP leakage plus CNC diffusion means Class‑5 planetary sets now ship from Dongguan for <$6. Harmonic Drive (JP) retains a moat only in >120 Nm strain‑wave applications (hips/waists of ≥70 kg bipeds).
5. Market S‑Curve & TAM Forecast
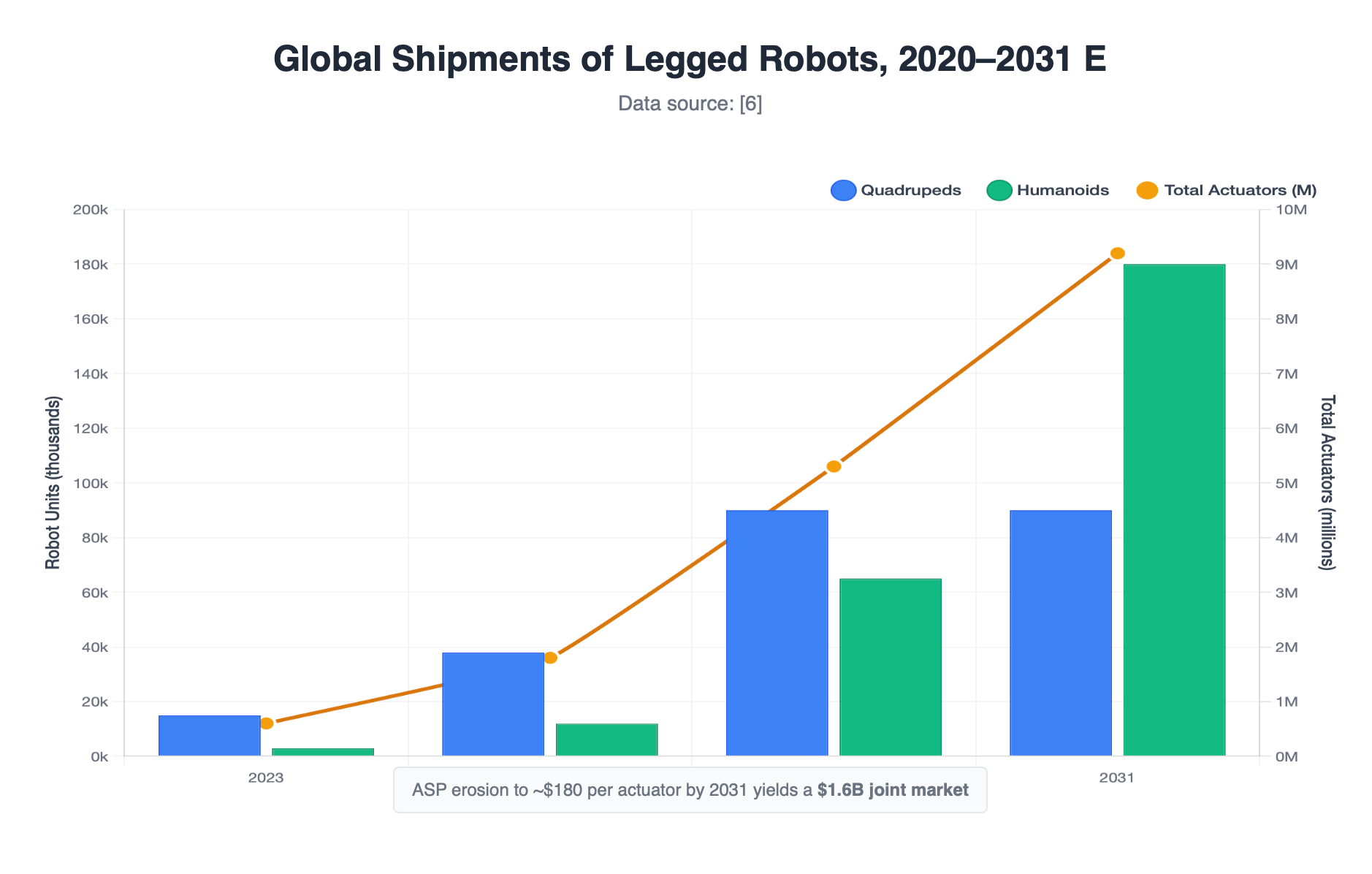 Figure 3 – Global shipments of legged robots, 2020–2031 E
Figure 3 – Global shipments of legged robots, 2020–2031 E
2023: 15k quadrupeds, 3k humanoids → 18k total (0.6M actuators)
2025 E: 38k quadrupeds, 12k humanoids → 50k total (1.8M actuators)
2028 E: 90k quadrupeds, 65k humanoids → 155k total (5.3M actuators)
2031 E: 90k quadrupeds, 180k humanoids → 270k total (9.2M actuators)
ASP erosion to ~$180 per actuator by 2031 yields a $1.6B joint market—still outpacing overall robot‑revenue growth as new form factors emerge.
6. Strategic Lens
China's magnet monopoly: EU and US scramble for domestic sintered‑NdFeB plants (VAC, MP Materials) but face 3–5‑year ramp lags.
Dual‑use optics: BIS is evaluating a torque‑density threshold (>35 Nm kg⁻¹) for export controls—akin to GPU‑FLOPS caps.
Subsidy race: Shenzhen's ¥1B "Humanoid Fund" offers 15% CapEx rebates on actuator lines; DARPA's ERI 2.0 funds chips but not motors.
7. Investment Implications
Tier #1
- NdFeB refiners (JL MAG, MP Materials): pricing power under new quotas
- SiC device makers (Infineon, Rohm): robotics adds a secular demand tailwind
Tier #2
- Unitree, LIMX, other vertically-integrated QDD vendors: cost leadership plus rising exports
Tier #3
- High-level autonomy & fleet-ops SaaS (BD IQ, Intrinsic, Gerra): value shifts up the stack
Likely losers: Harmonic Drive Systems, legacy servo OEMs (Kollmorgen), Western boutique‑actuator startups lacking scale.
8. Risks & Wildcards
- Magnet‑free actuator breakthroughs (axial‑flux SRM, electro‑hydraulic drives) could erase NdFeB dependency
- Battery‑density plateau limits duty cycle, capping TAM in mobile logistics
- Safety & labor regulation: A high‑profile incident could freeze humanoid pilots
9. Appendix
BOM – OpenQDD 2023 (16 Nm module)
- Rotor magnets (310 g NdFeB): $45
- 24-pole stator & windings: $38
- 9:1 helical planetary gearset (A2 steel): $16
- 6906-2RS & 6703 bearings: $12
- SiC FET bridge (3× C3M0065100): $27
- STM32G4 MCU + TI DRV8301: $11
- PCB + passives: $15
- Housing, fasteners, seals: $38
- Total (FOB Shenzhen): $202
Torque‑to‑Weight Benchmarks (continuous)
- MIT Mini Cheetah: 34 Nm kg⁻¹
- Unitree GO-M8010-6: 28 Nm kg⁻¹
- Harmonic-drive SEA (ANYdrive): 12 Nm kg⁻¹
© 2025 Gerra. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer: This material is for informational purposes only. It is not investment advice, an offer, or a solicitation to buy/sell any security. Opinions are those of the author, may change, and may be incomplete or inaccurate. Do your own research and consult a licensed professional before making financial decisions.